publications
2024
- Hardware-Software
 CAD Techniques for NoC-Connected Multi-CGRA SystemsHaron Wei , Omkar Bhilare , Hamas Waqar, and 1 more authorIn Highly Efficient Accelerators and Reconfigurable Technologies (HEART) , 2024
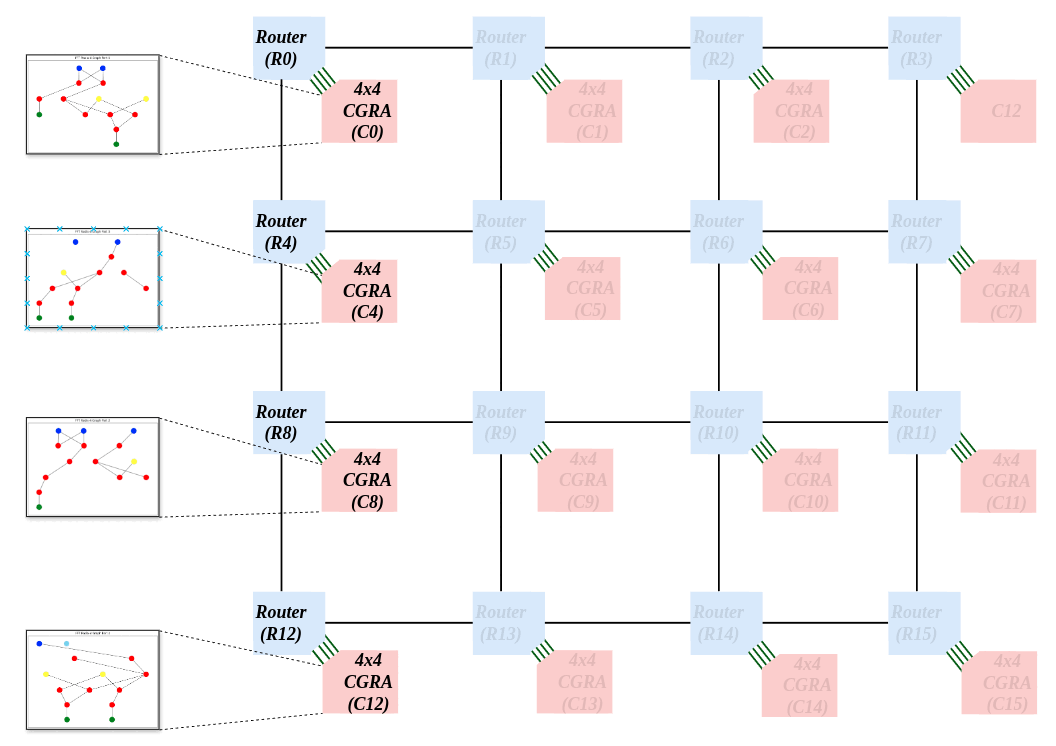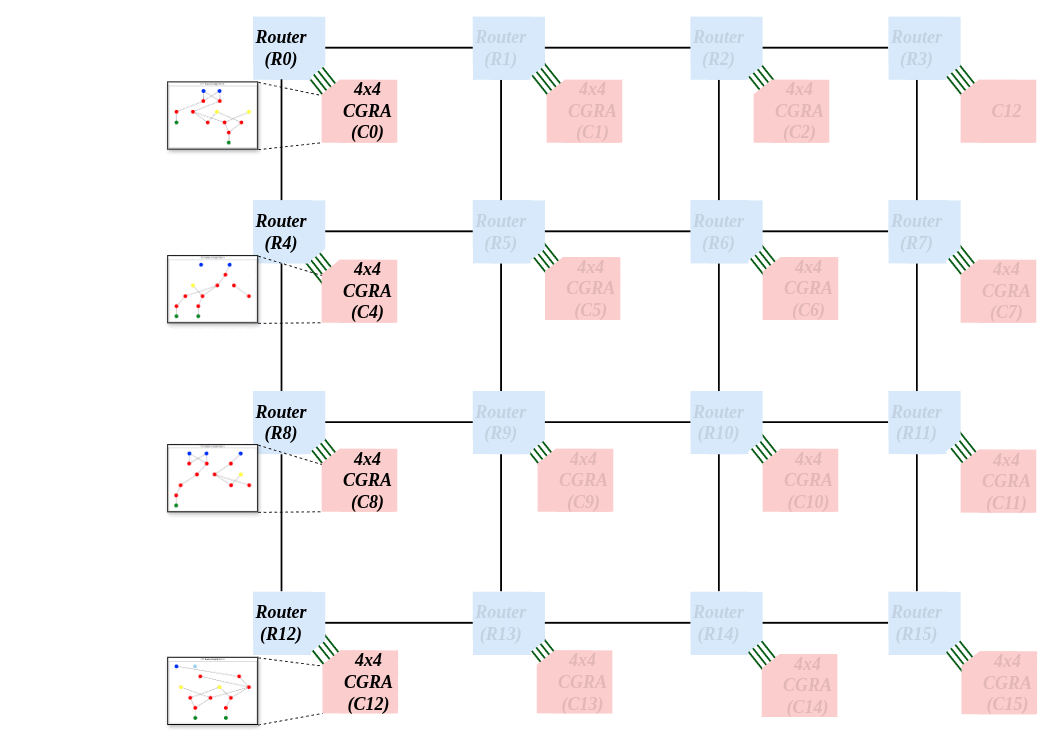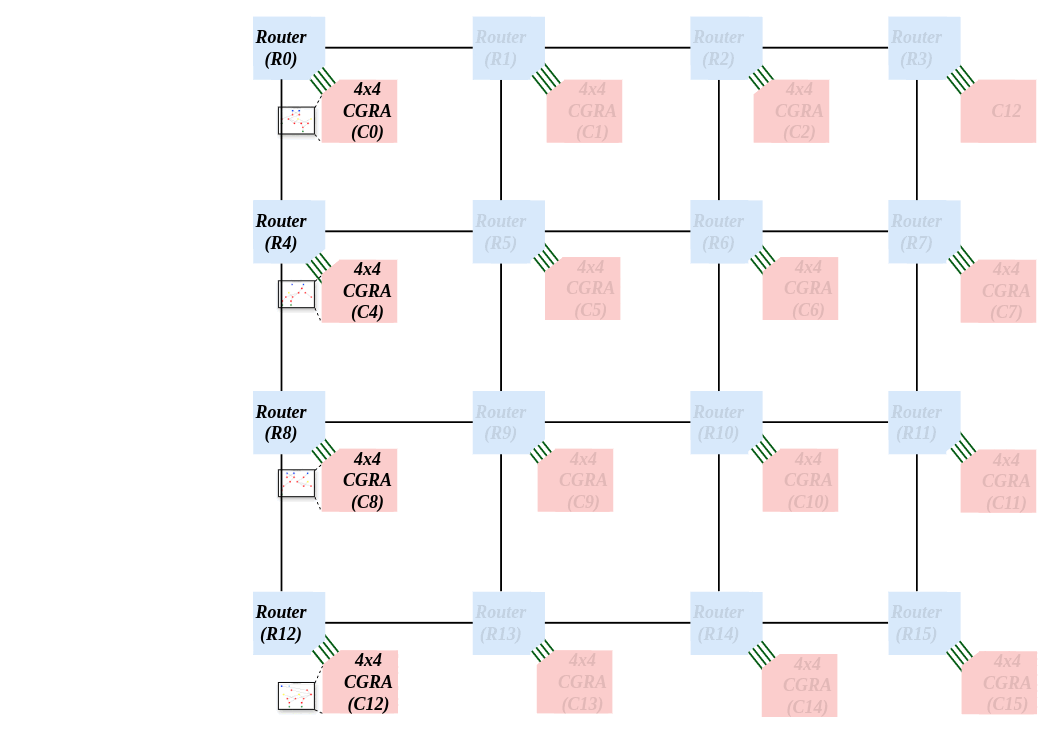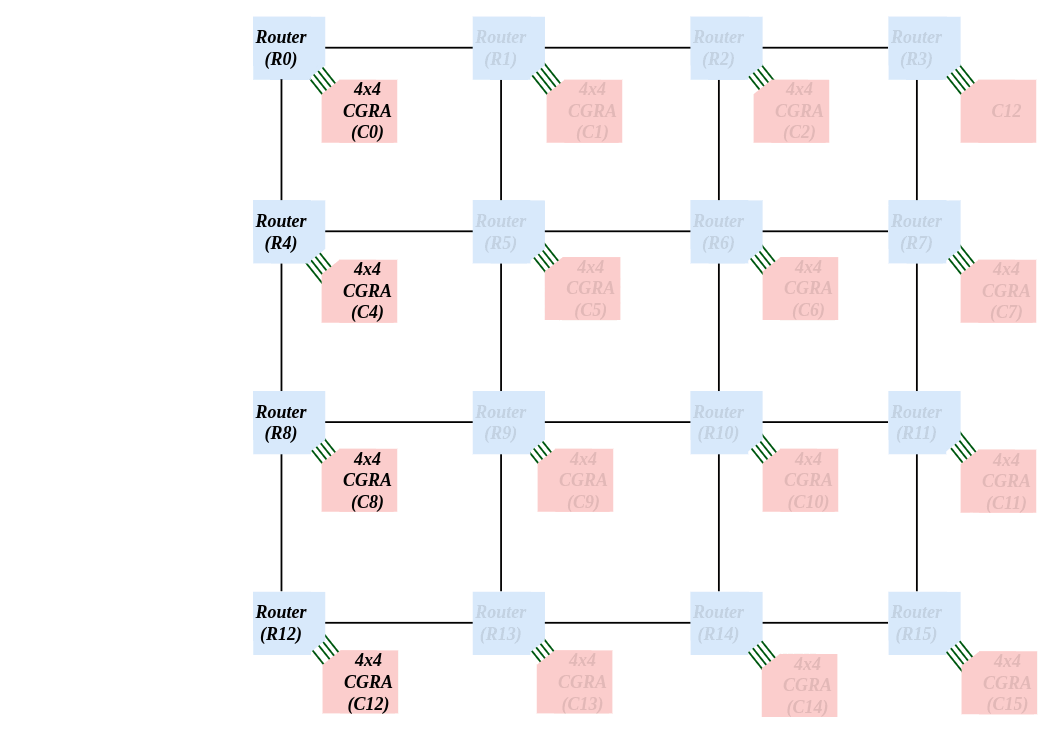
CAD Techniques for NoC-Connected Multi-CGRA SystemsHaron Wei , Omkar Bhilare , Hamas Waqar, and 1 more authorIn Highly Efficient Accelerators and Reconfigurable Technologies (HEART) , 2024Coarse-grained reconfigurable arrays (CGRAs) are programmable hardware platforms that are a means of realizing application accelerators. A CGRA is a 2D array of configurable processing elements (PEs), that connect to one another through programmable interconnects. PEs and interconnects in CGRAs are configurable at the word level, as opposed to at the bit level in FPGAs. A network-on-chip (NoC) is an on-chip communications system comprising routers and links, where data is packet-switched. NoCs provide more scalable communication vs. traditional on-chip busses or crossbars. In this paper, we propose an NoC-connected multi-CGRA system, where multiple modest-sized CGRAs communicate using an NoC. We introduce CAD techniques that partition and place an application across the “distributed” NoC-connected CGRAs. We study the quality and runtime of the CAD techniques on a system having sixteen 4 × 4 CGRAs connected together using a 2D mesh NoC.
@inproceedings{10.1145/3665283.3665297, author = {Wei, Haron and Bhilare, Omkar and Waqar, Hamas and Anderson, Jason}, title = {CAD Techniques for NoC-Connected Multi-CGRA Systems}, booktitle = {Highly Efficient Accelerators and Reconfigurable Technologies (HEART)}, year = {2024}, url = {https://camps.aptaracorp.com/ACM_PMS/PMS/ACM/HEART24/14/ed351247-1874-11ef-8182-16bb50361d1f/OUT/heart24-14.html}, doi = {10.1145/3665283.3665297}, }
2023
- Hardware-Software
 DEEPFAKE CLI: Accelerated Deepfake Detection Using FPGAsOmkar Bhilare , Rahul Singh , Vedant Paranjape, and 3 more authorsIn Parallel and Distributed Computing, Applications and Technologies , 2023
DEEPFAKE CLI: Accelerated Deepfake Detection Using FPGAsOmkar Bhilare , Rahul Singh , Vedant Paranjape, and 3 more authorsIn Parallel and Distributed Computing, Applications and Technologies , 2023Because of the availability of larger datasets and recent improvements in the generative model, more realistic Deepfake videos are being produced each day. People consume around one billion hours of video on social media platforms every day, and that’s why it is very important to stop the spread of fake videos as they can be damaging, dangerous, and malicious. There has been a significant improvement in the field of deepfake classification, but deepfake detection and inference have remained a difficult task. To solve this problem in this paper, we propose a novel DEEPFAKE C-L-I (Classification - Localization - Inference) in which we have explored the idea of accelerating Quantized Deepfake Detection Models using FPGAs due to their ability of maximum parallelism and energy efficiency compared to generalized GPUs. In this paper, we have used light MesoNet with EFF-YNet structure and accelerated it on VCK5000 FPGA, powered by state-of-the-art VC1902 Versal Architecture which uses AI, DSP, and Adaptable Engines for acceleration. We have benchmarked our inference speed with other state-of-the-art inference nodes, got 316.8 FPS on VCK5000 while maintaining 93% Accuracy.
@inproceedings{10.1007/978-3-031-29927-8_4, author = {Bhilare, Omkar and Singh, Rahul and Paranjape, Vedant and Chittupalli, Sravan and Suratkar, Shraddha and Kazi, Faruk}, editor = {Takizawa, Hiroyuki and Shen, Hong and Hanawa, Toshihiro and Hyuk Park, Jong and Tian, Hui and Egawa, Ryusuke}, title = {DEEPFAKE CLI: Accelerated Deepfake Detection Using FPGAs}, booktitle = {Parallel and Distributed Computing, Applications and Technologies}, year = {2023}, publisher = {Springer Nature Switzerland}, address = {Cham}, pages = {45--56}, google_scholar_id = {u5HHmVD_uO8C}, url = {https://www.hackster.io/thematrix/deepfakes-c-l-i-on-vck5000-f04ca2}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-031-29927-8_4}, isbn = {978-3-031-29927-8} }
